
Want to know how we increased our traffic over 1000%? If you’re not sure what version you’re working with, click on the ‘apple’ icon in the top-left corner of your desktop, and select About This Mac: This process varies based on which version of macOS you’re running. In order to clear the DNS cache on a Mac, you’ll need to open the native command-line interface known as Terminal and run the appropriate command.
#Cache cleaner for mac how to
Below, we’ve explained how to carry out this task for the macOS, Windows, and Linux Operating Systems (OSs), as well as on the Google Chrome browser. It also matters whether you need to flush it from your computer or your browser. How to Flush Your DNS Cache on Mac, Windows, Linux, and ChromeĬlearing your DNS cache is a relatively simple process, but it varies depending on your OS. Knowing how to clear your DNS cache could help you in many similar situations, it can fix errors like 304. We asked them to clear their DNS cache locally on their computer and refresh the page.Īt that point, everything started loading normally on their WordPress site again. We wanted to ensure that the site was loading fine everywhere, beyond just our physical location, and that it was resolving back to the client’s CDN provider.Īfter all this digging, we confirmed that there was a small change with the client’s DNS provider that was still cached on their end. This tool enables users to quickly check the resolution on DNS records (such as the CDN CNAME) from multiple geographical locations.
#Cache cleaner for mac free
We then ran the client’s CDN URL through the free whatsmydns tool. The first thing we did was ping the CDN subdomain to see if we could access it. Upon inspecting their site with Chrome Devtools, we could see that everything coming from their CDN subdomain ( ) wasn’t loading correctly, and instead was reporting 404 errors. The site appeared to be loading just fine for us, however, and the client hadn’t made any recent changes. The client reached out to us because their images, CSS, and JavaScript weren’t loading correctly on their website. To illustrate the point further, let’s look at an example that actually happened to a Kinsta client’s website. In any of these situations, clearing your DNS cache can often help you resolve the problem and get back online.
It can also simply become outdated or create internet connectivity issues. Unfortunately, your DNS cache may become corrupted, leading you into phishing schemes. This enables your browser to reload sites you’ve visited in the past more quickly than if it had to reference the DNS again each time. So, DNS caching involves your Operating System (OS) or browser capturing recently-visited IP addresses and saving them in a database. As for ‘caching’, it’s the process of saving a snapshot of something (such as a web page) so it can be reloaded faster in the future. You can think of it as a directory or phone book for websites.
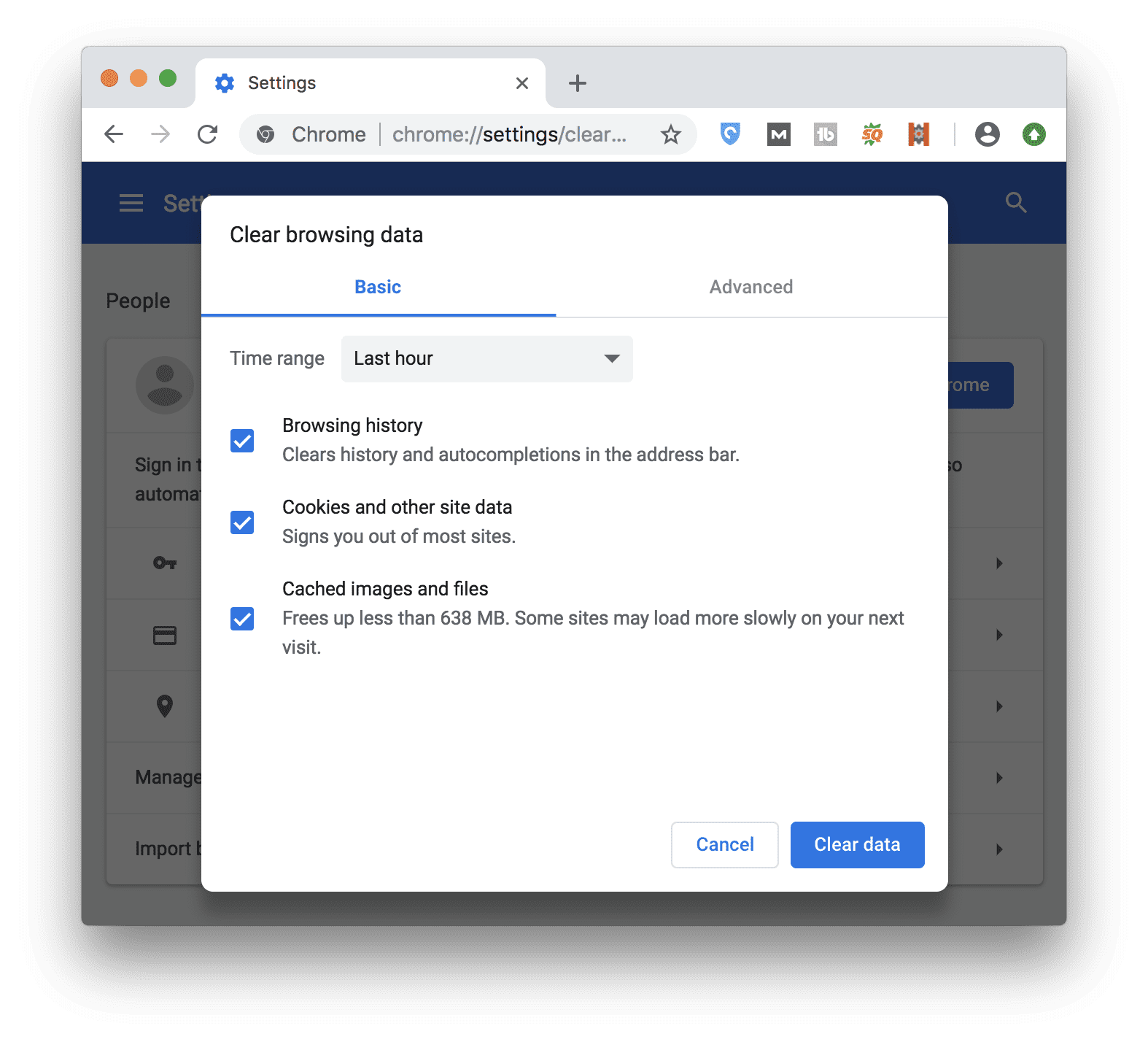
If you turn sync on in Chrome, you’ll stay signed into the Google Account you’re syncing to in order to delete your data across all your devices.For example, if you were signed in, you’ll need to sign in again. If you use Safari, Firefox, or another browser, check its support site for instructions. For example, you can delete cookies for a specific site. Learn how to change more cookie settings in Chrome. Next to "Cookies and other site data" and "Cached images and files," check the boxes.Clearing them fixes certain problems, like loading or formatting issues on sites. When you use a browser, like Chrome, it saves some information from websites in its cache and cookies.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
